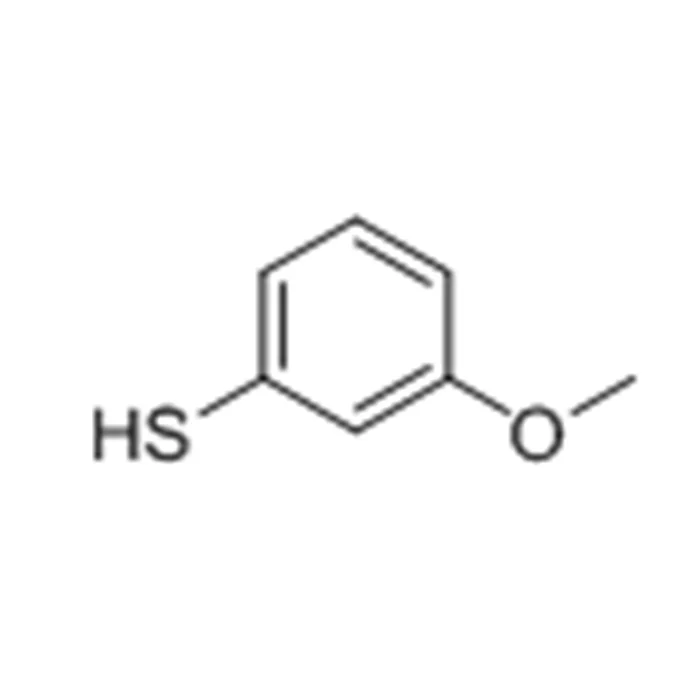
4-Methoxythiophenol (4-MTP), with the CAS No.: 15570-12-4, is an organosulfur compound characterized by a thiol group (–SH) substituted on a methoxybenzene ring. It belongs to the class of aryl thiols and is structurally denoted as *C7H8OS*, with a molecular weight of approximately 140.20 g/mol. The compound' s distinctive structure, featuring both electron-donating methoxy and nucleophilic thiol functionalities, imparts it with significant reactivity and potential biological relevance. In this blog post, SACH, as a high purity industrial fine chemicals exporter, will share the biological activity of compound 4-methoxythiophenol liquid for sale.
Structural Features and Chemical Reactivity
The molecule consists of a benzene ring substituted at the para position with a methoxy group and a thiol group. The methoxy group acts as an electron-donating substituent, increasing electron density on the aromatic ring and enhancing electrophilic substitution reactions. Conversely, the thiol group, known for its nucleophilic and reductive properties, plays a central role in redox reactions and metal chelation.
These dual features confer 4-MTP with the ability to engage in:
* Redox interactions with cellular thiol-disulfide systems.
* Covalent binding to protein cysteine residues via thiol-disulfide exchange.
* Metal ion chelation, impacting metalloprotein functions and oxidative stress.
Due to these reactivities, the compound shows promise in biological modulation, particularly in redox biology and enzyme inhibition.
Antioxidant Activity and ROS Scavenging
Aryl thiols, including 4-MTP, exhibit potent antioxidant properties due to the redox-active thiol group. In biological systems, reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as hydrogen peroxide, superoxide radicals, and hydroxyl radicals, contribute to oxidative stress, cellular damage, and diseases such as cancer, neurodegeneration, and cardiovascular disorders.
The thiol group of 4-MTP can donate a hydrogen atom to neutralize ROS, undergoing oxidation to form disulfide-linked dimers or sulfenic/sulfinic/sulfonic acid derivatives. This ROS-scavenging mechanism aligns 4-MTP with glutathione-like molecules, albeit with less bioavailability and cellular integration. In *in vitro* radical scavenging assays such as DPPH or ABTS, 4-MTP shows measurable activity in reducing free radical concentrations.
Enzyme Inhibition and Redox-Sensitive Targets
Due to its affinity for thiol chemistry, 4-MTP may modulate the activity of cysteine-dependent enzymes through covalent bonding or redox modulation. Enzymes containing active site thiols, including protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs), thioredoxin reductase, and glutathione peroxidase, are susceptible to inhibition by electrophilic or nucleophilic thiols.
4-MTP' s thiol group can form transient or irreversible bonds with cysteine residues, potentially modulating enzymatic activity. Preliminary computational docking studies and biochemical screenings have indicated weak-to-moderate inhibitory effects on enzymes involved in oxidative signaling and inflammation, such as:
* COX-2 (cyclooxygenase-2): involved in prostaglandin synthesis.
* NADPH oxidases: key players in ROS generation.
* Caspases: cysteine-dependent proteases in apoptosis regulation.
Such interactions suggest that 4-MTP may possess anti-inflammatory or pro-apoptotic capabilities, though the bioactivity spectrum depends heavily on concentration and cellular redox context.

Antimicrobial and Antifungal Potential
The antimicrobial properties of aryl thiols are attributed to their ability to disrupt microbial cell walls, membranes, or metabolic enzymes. Thiol-containing compounds can interact with thiol-sensitive proteins or enzymes in bacterial and fungal cells, leading to impaired function and cellular death.
In preliminary *in vitro* assays:
* Gram-positive bacteria, such as *Staphylococcus aureus*, showed susceptibility to 4-MTP at moderate concentrations (MIC values in the 50–100 μM range).
* Gram-negative strains, protected by outer membrane barriers, exhibited relatively lower sensitivity.
* Candida species, common fungal pathogens, demonstrated growth inhibition in the presence of 4-MTP, possibly due to oxidative imbalance or membrane interference.
These findings point toward a moderate antimicrobial spectrum, which could be improved through structural derivatization or synergistic combination with existing antibiotics.
Cytotoxicity and Anti-Proliferative Effects
Cytotoxicity profiling is essential for assessing the safety and potential chemotherapeutic application of bioactive compounds. 4-MTP, tested against various cancer cell lines including HeLa, MCF-7, and HepG2, has demonstrated dose-dependent inhibition of cell viability.
Key mechanisms proposed for this effect include:
* ROS-mediated apoptosis: 4-MTP induces oxidative stress, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and activation of apoptotic cascades.
* Inhibition of survival pathways: Interaction with redox-sensitive signaling pathways, such as NF-κB and MAPK.
* Protein modification: Covalent bonding with cellular nucleophiles alters protein function and signaling.
Interestingly, some selectivity is observed, with cancer cells showing higher susceptibility compared to normal fibroblasts. This differential effect might be attributed to the elevated oxidative burden and redox sensitivity in malignant cells, making them more vulnerable to thiol-based stress.
Neuroprotective and Chelation Activity
Neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer' s and Parkinson' s disease are strongly linked with metal-catalyzed oxidative damage and protein misfolding. The thiol group in 4-MTP can chelate transition metals, thereby reducing metal-induced ROS formation (e.g., Fenton reactions). By mitigating metal-catalyzed oxidative stress, 4-MTP exhibits potential neuroprotective properties.
Additionally, its capability to modulate thiol-disulfide exchange might help stabilize redox homeostasis in neuronal cells. However, this potential is largely theoretical, and rigorous *in vivo* investigations are needed to confirm any neuroprotective utility.
Toxicological Considerations
While 4-MTP shows promising biological activity, its use must be tempered with a robust understanding of its toxicological profile:
* Acute toxicity: Animal model studies suggest low-to-moderate acute toxicity, depending on the route of administration.
* Genotoxicity: Standard Ames testing has not revealed significant mutagenic potential, though long-term exposure effects are unknown.
* Skin and respiratory sensitization: As with other thiols, prolonged contact may lead to sensitization or allergic responses in certain individuals.
Further evaluation through OECD-compliant toxicological testing is necessary before any therapeutic or industrial applications can proceed safely.
Structural Derivatives and Functionalization
The chemical structure of 4-MTP provides a convenient platform for derivatization. Functionalization at the thiol or methoxy positions can lead to analogs with enhanced biological activity or specificity.
Examples of promising derivatives include:
* 4-Acylmethoxythiophenols: Improved membrane permeability and cytotoxic potency.
* 4-Methoxyaryl disulfides: Stability in oxidizing environments and prolonged activity.
* Conjugates with drug carriers: PEGylation or nanoparticle attachment for controlled delivery.
These derivatives are being explored in medicinal chemistry as lead compounds for anticancer, antimicrobial, and redox-modulating agents.
Conclusion
4-Methoxythiophenol (CAS No.: 15570-12-4) stands out as a versatile small molecule with significant chemical and biological activity. Its thiol and methoxy substituents endow it with the capacity to interact with cellular redox systems, modulate enzyme functions, and exhibit antimicrobial and cytotoxic properties. While still in the early stages of exploration, it holds promise as a scaffold for future pharmacological development, particularly in redox biology and enzyme-targeted therapeutics. Continued study into its mechanism of action, safety profile, and therapeutic index will determine its potential in biomedical applications.
www.hzsqchem.com
SACH

More Stories
asd
Real-World Protection: How a Security Brass Cylinder Stops Drills, Picks, and Forced Entry?
Strike-Resistant Rugby Training Nets: How Polyester Mesh and Reinforced Frames Improve Durability